A stable and reliable drive control system is crucial for ensuring the operation of telescopes, directly impacting the successful conduct of continuous astronomical observations. Therefore, reliability is a key indicator in evaluating telescope performance.
The research team from Nanjing Institute of Astronomical Optics & Technology (NIAOT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has conducted in-depth theoretical studies on systematically enhancing drive control reliability.
They have proposed a multidimensional proactive strategy for improving telescope reliability. This strategy addresses three aspects: solutions for anticipated faults, handling strategies for unanticipated states, and proactive optimal designs.
These three methods complement each other, systematically enhancing the reliability of telescope drive controls. Such a multidimensional proactive reliability enhancement strategy is particularly suitable for the actual operation of large telescopes, applying targeted technical measures at different angles and stages to improve reliability.
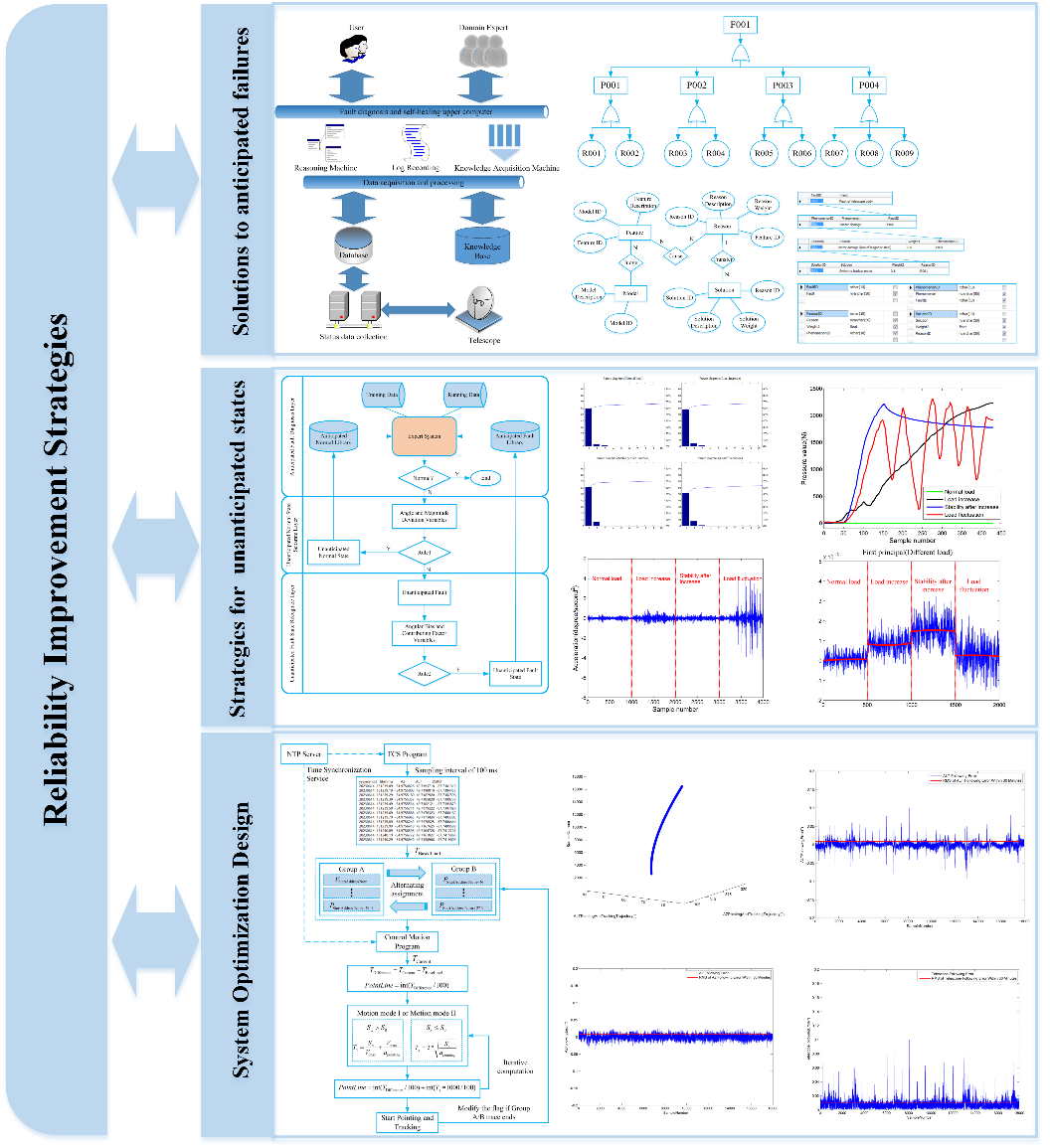
Figure 1: A Reliability Enhancement Strategy Mechanism for Telescope Drive Control Systems Based on Solutions for Expected Faults, Strategies for Handling Unexpected States, and Proactive Optimization Designs.
Diagnosis and self-healing technologies for anticipated faults significantly enhance maintenance efficiency, thereby reducing mean time to repair and indirectly improving system operational reliability.
Strategies for handling non-anticipated states leverage data mining to underscore their advantages in scenarios where explicit variable analysis fails to effectively identify issues, serving as another approach to enhance system reliability.
Solutions for anticipated faults and strategies for addressing non-anticipated states function merely as auxiliary measures to bolster reliability during the operational phase. The critical path to fundamentally elevate reliability lies in optimizing system design based on weaknesses identified during diagnosis and maintenance.
This optimization encompasses not only hardware design improvements but also software algorithm refinement and adjustments to maintenance strategies. Common optimization methods include redundancy design, tracking strategy optimization, and program simplification. These methodologies are increasingly being integrated into the design of telescope drive control systems.
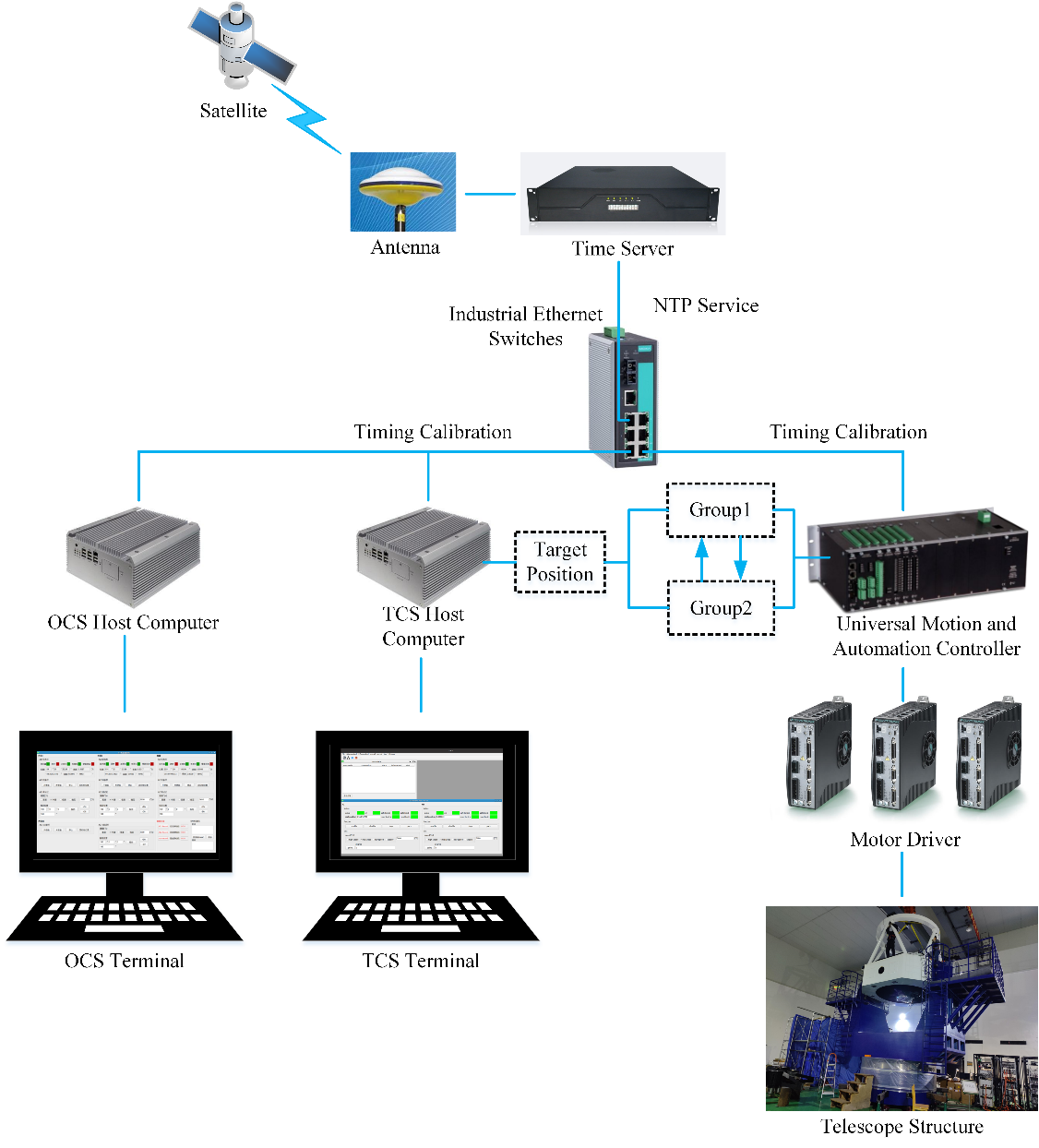
Figure 2: OPTIMIZED STRATEGY FOR TELESCOPE TRACKING CONTROL UNDER TIMESTAMP SYNCHRONIZATION METHOD: PACKET-BASED TRANSMISSION OF TARGET POSITION
China's next-generation large optical-infrared telescope plans to develop an independent reliability management unit subsystem to assist in improving its operational reliability. This research can provide technical accumulation for the telescope.
The research findings, titled "Reliability Improvement Strategies for Telescope Control Systems," were published in the international astronomy journal Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific. Dr. Yun Li is the first author of the paper, and Researcher Yang Shihai is the corresponding author. The article was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos.: 12303089, 11973065) and the Jiangsu Excellent Postdoctoral Program (No.: 2022ZB449).
Paper Information
Citation: Li Yun et al 2025 PASP 137 015001
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1088/1538-3873/ada704