Recently, Dr. Hu Tianzhu, Prof. Zhang Yong and academician Cui Xiangqun (academician of Chinese Academy of Sciences) from Nanjing Institute of Astronomical and Optical Technology (NIAOT) have proposed a new method to conduct real-time monitoring telescope performance based on LAMOST star guide camera data and machine learning algorithm. In astronomy, the demand for high-resolution imaging and high-efficiency observation requires telescopes that are maintained at peak performance. To improve telescope performance, it is useful to conduct real-time monitoring of the telescope status and detailed recordings of the operational data of the telescope. At present, common monitoring method for telescope performance mainly depends on pictures captured by the acquisition camera or science camera through manual monitoring or alarm through setting the parameter threshold of the sensor, but it was not able to meet the requirements of intelligent real-time monitoring of the new kind of telescope. Based on the data of guide star camera of LAMOST, a new method on intelligent real-time monitoring for telescope performance by using machine learning has been put forward. The core of the technology is to establish the corresponding relationship between telescope performance and star image shape. Machine learning algorithm is used to classify star image shape in real time to monitor the overall performance of telescope. Through testing and analysis, conclusion can be given that real-time monitoring of LAMOST including guiding system performance, focal surface defocus, offset of segmented mirror and active optics system performance has been realized. The ultimate performance detection accuracy can reach up to 96.7 percent. 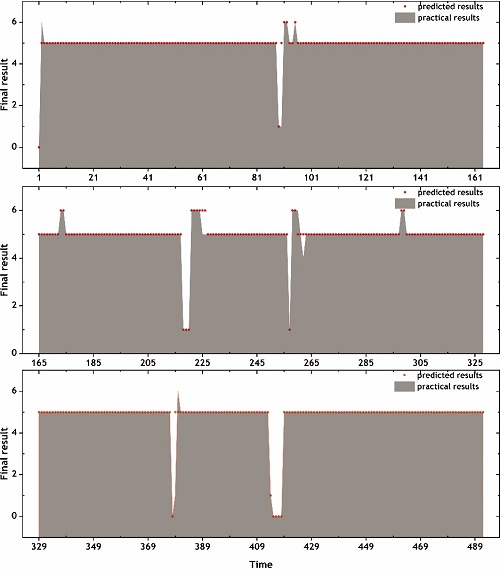
Performance of monitoring for LAMOST by new method paper: https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2020MNRAS.500..388H/abstract |