LAMOST High Resolution Spectrometer (hereafter referred to as L-HRS) developed jointly by National Observatory, Chinese Academy of Sciences and Nanjing Institute of Astronomical and Optical Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences finished construction and passed specialist check and acceptance organized by CAS in September 2018. The design of the L-HRS takes into account the high spectral resolution and the high star light acquisition rate. 1): Fiber with 4.5 "large Core diameter used to increase star acquisition rate 2): 2-slicing image slicer (4.5 "= 2 x 2.25", shown in figure 1) before slit used to solve the problem between the high spectral resolution and the high star light acquisition rate for realization of high spectral resolution under Unlimited slit 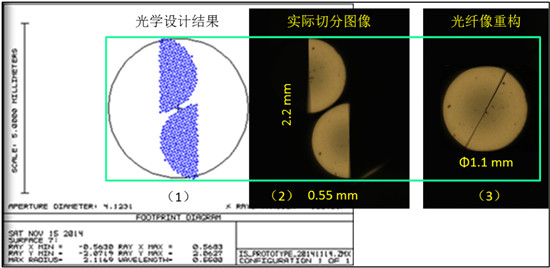
figure 1 2-slicing image slicer before slit 3): Segmented deep groove echelle grating (R4) as the main dispersion element with 200x800mm diffraction area adopted to provide twice dispersion power compared to conventional single echelle grating with 200x400mm diffraction area 
figure 2 Segmented deep groove echelle grating with 200x800mm diffraction area 4): Combination of volume phase holographic grating (VPHG) and independent triangular prism used as lateral dispersion element to improve the difference of the order interval between red and blue channel 
figure 3 LAMOST High Resolution Spectrometer Recently, L-HRS carried out trial high-resolution observation of special objects during the large moon night and effectively obtained the high-resolution (R~ 40000) and high signal-to-noise ratio spectra of two lithium-rich giant stars with the magnitude of about 10. 
figure 4 two-dimensional image of the lithium-rich giant star 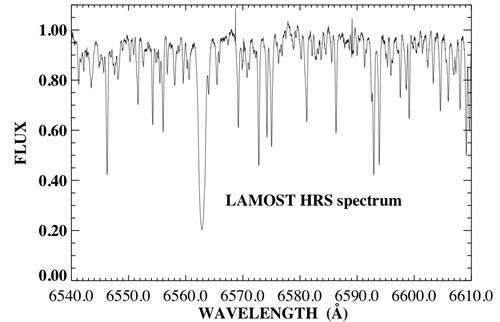
figure 5 Hα spectrum of the lithium-rich giant star 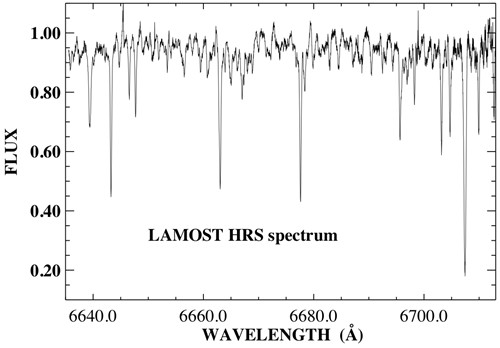 figure 6 powerful lithium spectrum of the lithium-rich giant star we will use L-HRS to conduct high-resolution observation of special objects during the large moon night and start high-resolution observation for stars with the magnitude of brighter than 12.5 during official survey. |